Using SSH to Connect to Our Class Server
Server Name/Port number will be in your Canvas Course Page
Basic Concepts
- SSH (Secure SHell) has been around for a while. It is a protocol that allows for encrypted connections to remote machines (often running Linux/Unix or BSD flavors (Mac has a BSD origin))
- Microsoft has not really supported SSH at all, until recently, via Powershell
- you need a SSH client software to connect to the remote machine, where you can do work
- Even if you use something like MySQL Workbench, that program needs to use SSH to connect to the machine that runs our database software
Mac OSX/Linux
Initial Set Up
- You need to create a
.sshfolder inside your home directory - on linux that is usually
/home/username - on mac it is often
/Users/username - Copy your private key (which ends in .pem for our example) into that .ssh folder
- Open up the terminal
cd ~should take you to your users home directorypwdwill give you your present working directory (it is just information, this command does not make any changes)mkdir .sshto make the folder/directory if you have not already done so- Move your key file into the new .ssh folder somehow
- use the file manager gui tool (whichever one you use)
- use the
cpcommand- if your file is in your downloads folder on Mac/Linux
cp ~/Downloads/filename.pem ~/.ssh/
- if your file is in your downloads folder on Mac/Linux
cd .sshchmod 600 filename.pem
Using SSH
- Using the terminal
ssh -i ~/.ssh/filename.pem username@host.name.com -p 22- replace filename.pem with the name of your keyfile (assuming you put it in a .ssh folder in your home directory)
- replace username with your actual username
- replace host.name.com with the actual hostname of the server
- while 22 is the default port, make sure you use the ACTUAL port # for the server
- When you first connect, it will ask you to store the servers public key, type yes (not just y but the complete yes)
- You can then connect to your MySQL Database using:
mysql -u username -p, again, replace username with your Real Username - the prompt should now look like
mysql> - If you want to change your MySQL password, at the
mysql>prompt type ALTER USER username Identified By 'passwordyouwanthere';and obviously put the password you want in the quotes.- When done with MySQL
quitand to get out of the SSH justexit
Using SFTP at the command line
- Note, if you can get Filezilla to work on Mac/Linux, that is probably easier, especially for beginners, but, if for some reason you can not get it working:
- You can still upload and download files with the sftp command instead of Filezilla
- You must have already done the
.sshfolder set up above sftp -i ~/.ssh/filenmame.pem -P 22 username@host.name.com(again, replace filename.pem, 22, username and host.name.com as needed)- Commands on the "remote" server when connected via sftp
lslists the contents of the remote directory (your target)pwdlists the directory you are in on the remote machinecd directorynamewill try to change the target directory on the remote machinecd ..will move you up one level in the directory/folder tree on the remote machine- How to do things on your "local" machine while connected
llslists the contents of present local directory, usually the one you started sftp insidelpwdlist the local directory that is presently activelcd directorynamewill try to change your local (source) directorylcd ..will move you up one level in the directory/folder tree on your local machine- Moving files
put filename.whateverwill try to upload the filname.whatever from your local directory to the remote directoryget filename.whateverwill try to download filename.whatever from the remote directory to your local directory- When done type
quit
Windows
Initial Set Up
- If you are using windows, you need to get Putty.exe. Either get the .msi version (64bit x86) or just get the putty.exe (64bit x86 stand alone).
- When you save the file, it will usually be in your Downloads directory, find it and run the file
- If it is the .msi version, you will actually install it and it will be added to your menu
- However, the putty.exe version is a stand alone and will just run when you double click on it
Using the Putty SSH Client
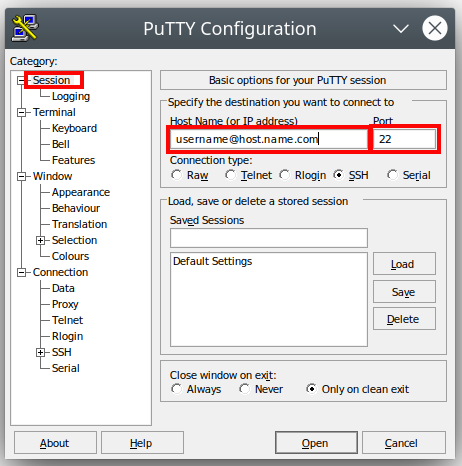
- When you first fire up putty, the Putty Configuration window opens up
- The left menu (Category:) will be on Session, and you need to use the school server name for the Host Name, the port # in the "Port" section
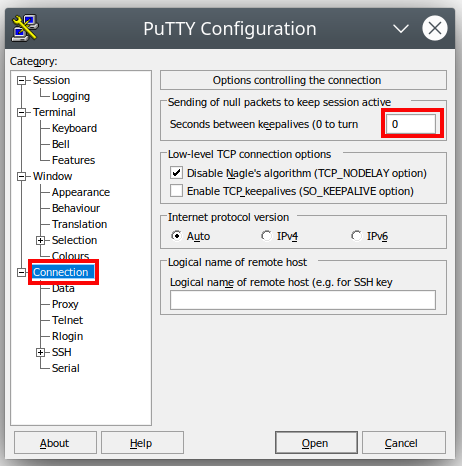
- Then click on "Connection* in the left side Menu
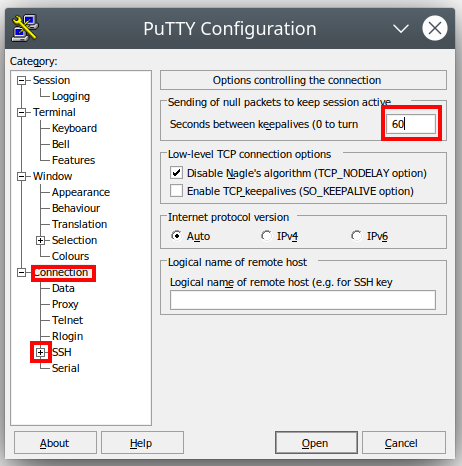
- For "Seconds Between Keepalives" change the 0 to 60
-
(You can also click on "Appearance" in the left menu and choose "Change" to alter the font size if you wish)
-
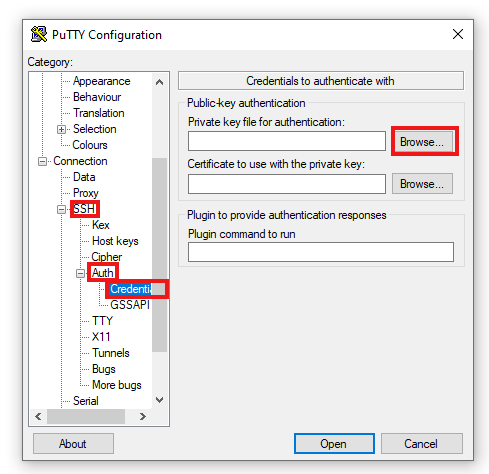
You need to set up the SSH encryption key, which has a .ppk ending, this will be under "Connection->SSH->Auth->Credentials"
- Before you connect, you can save your connection settings
- Type whatever name you can remember into the "Saved Sessions" window and click "save"
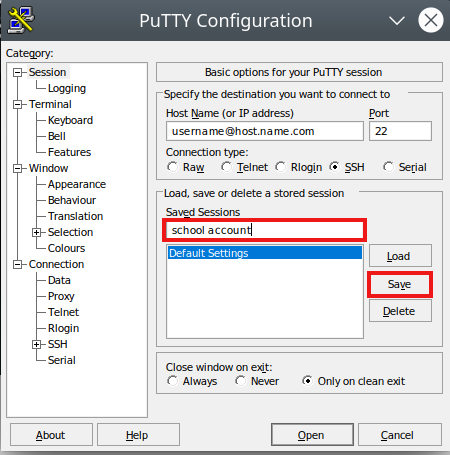
- Next time you open putty, click on the name of your session, and hit "Load"
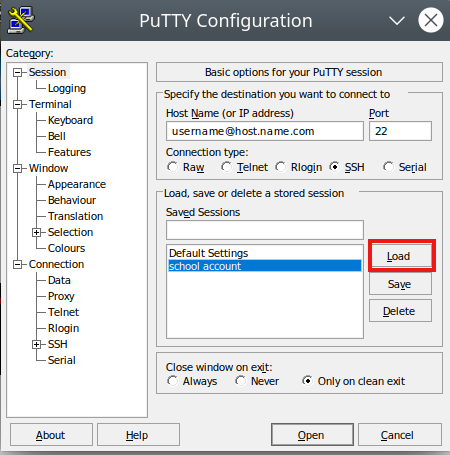
- Click "Open" to start your connection
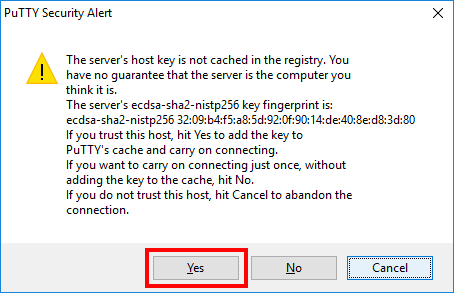
- As this is your first time connecting to the server, some form of warning will pop up, just agree with it.
- If everything works, you should see the command prompt like this: [username@nbtl ~]$
(Note: Image is from the old torchwood server)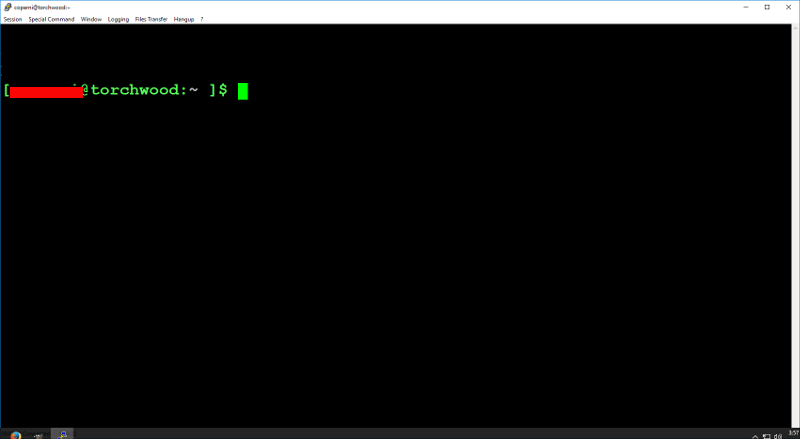
Connecting to MySQL once you are on the School Server
-
Using the command line SSH or Putty, once connect the rest is the same for everyone
-
type the command
mysql -u username -pwhen you are at the linux command prompt
- If it works, you should see mysql> on the screen
- If you want to change your msyql password:
ALTER USER username Identified By 'passwordyouwanthere';
- When done with MySQL just type
quitwhich will return you to the Linux Shell Prompt exitto shut down your SSH connection


