First Database Table
Create a simple example
First Table
- This will be a table that really should be split into many tables, this is just for getting used to creating tables and doing simple queries
- Table Name: products
- Fields
- product_id
- product_name
- product_desc
- product_price (may not belong in here?)
- product_category (really does not belong in here)
- product_quantity (may also not belong here)
- Design Table
- which storage engine to use (for MySQL use InnoDB, but there are others)
- storage engine determines what features exist for the table (FKs, triggers etc)
- Default Character Set (utf8 and collation utf8_general_ci or utf8_bin, utf8mb4 and utf8mb4_general_ci)
- MySQL Character Sets
- For Full utf8 Support you need to use utf8mb4 and utf8mb4_unicode_ci
- utf8mb4 Character Set Mysql.com
- comparision of utf8 character sets and why to use utf8mb4_unicode_ci
- How to support full Unicode in MySQL Databases
-
MySQL UTF8 Character Sets and Collations Explained
/* specify WHICH database to use */ /* Obviously, put in YOUR database name, which you can find with */ SHOW DATABASES; use STUusername; CREATE TABLE zproducts( product_id INT UNSIGNED PRIMARY KEY auto_increment, prod_name varchar(30), prod_desc varchar(255), price decimal(10,2), prod_cat varchar(20), quantity INT, SKU INT UNSIGNED, UNIQUE KEY(SKU) ) engine=InnoDB Default charset utf8mb4 collate=utf8mb4_unicode_ci; /* Lists tables in the present database */ show tables; /* Shows fields and field types for a table */ describe zproducts; /* Gives the SQL code to create the table It will be one complete statement, even if you have used a mix of CREATE, ALTER and so onto originally create the table Also includes a AUTO_INCREMENT=7 which specifies the PK value of the next insert if you use auto_increment */ show create table zproducts;
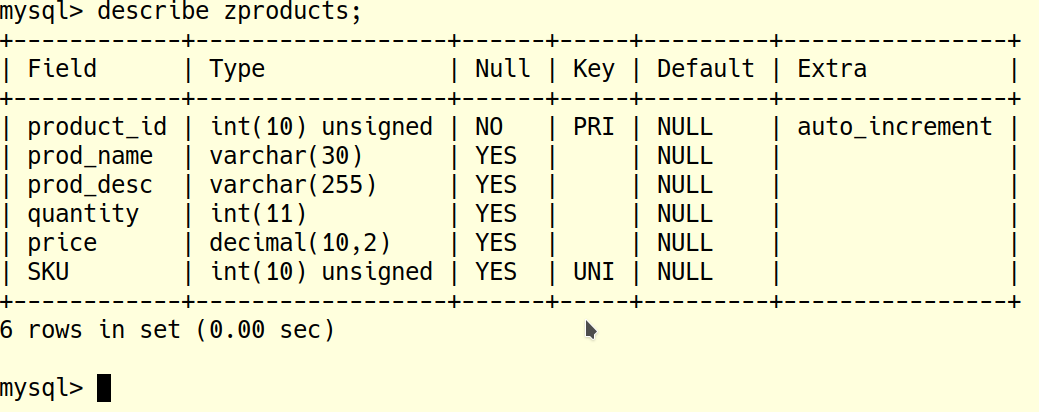
To Do an Insert
- Warning: Many old examples do not specify the fields you are inserting
- This means you have to put ALL the values in (even if empty), and in the order they are in the table
- You have to pass an empty field to the PK even if auto_increment
- This triggers warnings which slow the insert
- NOTE: If using auto_increment for your PK, you usually leave out the PK field in your insert
- You can specify the specific PK value you want, but that is rare
- If you delete a record, that PK value is not used again by auto_increment
-
NOTE: If you are doing multiple inserts at once, and some of them may fail, you can choose to add the IGNORE keyword after INSERT
INSERT INTO zproducts (prod_name,quantity,price) VALUES ('fusebox',23,23.95); INSERT INTO zproducts (prod_name,quantity,price) VALUES ('conduit',123,3.95), ('monitor',34,112.95), ('electrical tape',345,2.97);
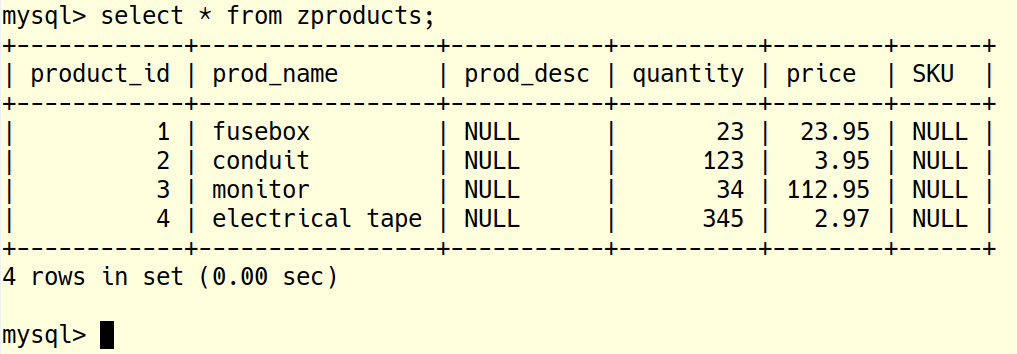
Simple SELECT queries
select * from zproducts; select prod_name,quantity,price from zproducts; select prod_name,quantity,price, quantity*price as Total from zproducts; select sum(quantity*price) as Total from zproducts;
UPDATE Example
UPDATE zproducts set prod_desc="An Electricians Friend" WHERE product_id=4; # *WARNING* if you forget the where clause # you change the entire table # Having to know the product_id is not very human friendly so a better update would be: UPDATE zproducts set prod_desc="An electrician's best friend" WHERE prod_name = "electrical tape"; # Oddly, there is a limitation on using subqueries (a query within a query) with updates and deletes, you can not use a table in the subquery, that is the one being updated, so this fails # Note, it is really overkill to use a subquery here regardless UPDATE zproducts set prod_desc="An Electricians Friend" WHERE product_id = (SELECT a.product_id FROM zproducts as a where a.prod_name = "electrical tape"); # Now, if you nest that table in yet another query, you can pull it off, but it is very ugly # and each time you use "zproducts" you have to give it an alias (as a, as b) which loads # another copy into memory. Really inefficient UPDATE zproducts set prod_desc="An Electricians Friend" WHERE product_id = (select PID FROM (SELECT a.product_id as PID FROM zproducts as a where a.prod_name = "electrical tape") as b); # The cleaner way to do this, would be to create a function like "getprodid()" that takes the # name and returns a product_id, but the simple where clause using the "prod_name" is the way to go
SELECTS WITH WHERE FILTERS
SELECT prod_name,quantity,price FROM zproducts WHERE price < 20; SELECT prod_name,quantity,price FROM zproducts WHERE price like "%97";
DELETE Examples
- Even more dangerous than UPDATE
- If you forget a "WHERE" clause here, you can delete the entire dataset from a table
-
Test with a select first (NOTE: do not actually delete product_id 1)
# Note, there is no undo, so always be careful with Deletes DELETE FROM zproducts WHERE product_id = 1; # Safer to try this first SELECT * FROM zproducts WHERE product_id = 1; # This will wipe out all your data in the table DELETE FROM zproducts;
Deleting multiple records at once
-
BE VERY CAREFUL to test this with a SELECT first
# first make some serious duplicates, as we have inserted no SKU values, which are our only UNIQUE KEY field, it is easy to create duplications # Do both of these to create 6 duplicate lines INSERT INTO zproducts (prod_name,quantity,price) VALUES ('conduit',123,3.95), ('monitor',34,112.95), ('electrical tape',345,2.97); INSERT INTO zproducts (prod_name,quantity,price) VALUES ('conduit',123,3.95), ('monitor',34,112.95), ('electrical tape',345,2.97); # check to see what our product_id's are, you should have 1 through 10, but may change depending on what you do SELECT * FROM zproducts;
Using the IN() function
# You can use the IN() operator to match multiple values DELETE FROM zproducts where product_id IN (5,6,7); # similar to using a series of "OR" statements
USING BETWEEN AND
# You can also do a range using BETWEEN AND DELETE FROM zproducts where product_id BETWEEN 5 AND 10; # this includes the end points, so 5,6,7,8,9,10 will get deleted # But those will only be deleted if they EXIST obviously, otherwise values that don't match in the range are ignored
USING WHERE
DELETE FROM zproducts where product_id >= 5 and product_id <=10; # same effect as the BETWEEN 5 AND 10


